Day 15: Linked List - HackerRank 30 days of code solution
Objective
Today we're working with Linked Lists. Check out the Tutorial tab for learning materials and an instructional video!
Today we're working with Linked Lists. Check out the Tutorial tab for learning materials and an instructional video!
A Node class is provided for you in the editor. A Node object has an integer data field, , and a Node instance pointer, , pointing to another node (i.e.: the next node in a list).
A Node insert function is also declared in your editor. It has two parameters: a pointer, , pointing to the first node of a linked list, and an integer value that must be added to the end of the list as a new Node object.
Task
Complete the insert function in your editor so that it creates a new Node (pass as the Node constructor argument) and inserts it at the tail of the linked list referenced by the parameter. Once the new node is added, return the reference to the node.
Complete the insert function in your editor so that it creates a new Node (pass as the Node constructor argument) and inserts it at the tail of the linked list referenced by the parameter. Once the new node is added, return the reference to the node.
Note: If the argument passed to the insert function is null, then the initial list is empty.
Input Format
The insert function has parameters: a pointer to a Node named , and an integer value, .
The constructor for Node has parameter: an integer value for the field.
The constructor for Node has parameter: an integer value for the field.
You do not need to read anything from stdin.
Output Format
Your insert function should return a reference to the node of the linked list.
Sample Input
The following input is handled for you by the locked code in the editor:
The first line contains T, the number of test cases.
The subsequent lines of test cases each contain an integer to be inserted at the list's tail.
The first line contains T, the number of test cases.
The subsequent lines of test cases each contain an integer to be inserted at the list's tail.
4
2
3
4
1
Sample Output
The locked code in your editor prints the ordered data values for each element in your list as a single line of space-separated integers:
2 3 4 1
Explanation
, so the locked code in the editor will be inserting nodes.
The list is initially empty, so is null; accounting for this, our code returns a new node containing the data value as the of our list. We then create and insert nodes , , and at the tail of our list. The resulting list returned by the last call to is , so the printed output is
The list is initially empty, so is null; accounting for this, our code returns a new node containing the data value as the of our list. We then create and insert nodes , , and at the tail of our list. The resulting list returned by the last call to is , so the printed output is
2 3 4 1.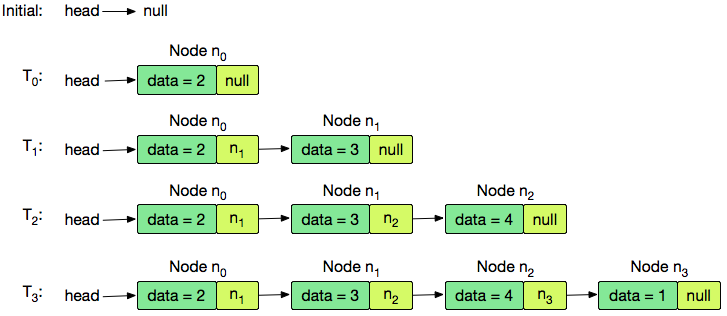
Solution :
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
class Solution {
public static Node insert(Node head,int data) {
if(head == null){
head = new Node(data);
}
else{
Node curr = head;
while(curr.next!=null){
curr = curr.next ;
}
curr.next = new Node(data);
}
return head;
}
public static void display(Node head) {
Node start = head;
while(start != null) {
System.out.print(start.data + " ");
start = start.next;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Node head = null;
int N = sc.nextInt();
while(N-- > 0) {
int ele = sc.nextInt();
head = insert(head,ele);
}
display(head);
sc.close();
}
}
Comments
Post a Comment